A stroke happens when blockages disrupt blood flow in the brain or when a blood vessel bursts, causing hemorrhaging in and around the brain. Often occurring suddenly and with little warning, a stroke can have devastating consequences if not treated quickly and effectively. In just a matter of minutes, a stroke can have significant impacts on a person’s physical, cognitive, and emotional well-being.
While medical interventions play a crucial role in addressing the acute symptoms and treatments for strokes, physical therapy is often an essential component of care for long-term recovery, rehabilitation, and overall health. Here, we will review some common causes and effects of strokes and how physical therapy benefits recovery and rehabilitation.
The Impact of a Stroke on The Human Body
Strokes happen when the brain doesn’t receive enough oxygen to function correctly. This can occur due to a blood clot blocking a blood vessel, known as an ischemic stroke, or from a busted blood vessel, leading to a hemorrhagic stroke. Regardless of which instance is responsible for the stroke, the brain begins to deteriorate rapidly as 2 million brain cells start to die each minute. When treating a stroke, time is of the essence as the brain and body fight to maintain bodily and cognitive function.
Strokes can cause individuals to experience a wide range of impairments, such as:
Motor Deficits: Injuries in the brain can cause weakness, paralysis, and difficulty with movement. After a stroke, many patients require rehabilitation to regain their ability to hold objects, walk, or even feed themselves.
Sensory Impairments: When brain signals to the nervous system are impacted, stroke patients may experience numbness, tingling, or reduced sensation to sensory stimulation.
Cognitive Impairments: During and after a stroke, the brain’s oxygen deprivation can lead to damage, potentially impairing the patient’s cognitive abilities. Patients may experience difficulty with thinking, memory, and problem-solving. In many cases, patients may experience cognitive impairment beforehand, causing them to ignore any warning signs or symptoms of an impending stroke.
Communication Impairments: Often a result of sensory, motor, and cognitive impairment, strokes can make communication and speech extremely difficult for stroke patients. Using multiple areas of therapy, stroke patients can often relearn how to talk or communicate over time.
Recognizing The Signs of a Stroke
Identifying the symptoms of a stroke is imperative in preventing long-term damage to the brain and body. As oxygen flow is interrupted, the brain is immediately at risk, causing the body and nervous system to exhibit warning signs and indicators of stroke.
The American Stroke Association encourages people to use F.A.S.T to help people identify and evaluate symptoms of a stroke and receive help promptly:
Face Drooping: If one side of the face is droopy or numb, it may indicate a brain injury in one side of the brain. If you suspect that someone has a stroke, ask them to smile. If their smile is uneven, they may be having a stroke.
Arm Weakness: Evaluate for arm weakness on one side of the body. If the patient cannot raise both arms equally, this can indicate neurological damage.
Speech Difficulty: Slurred speech and an inability to form coherent sentences can indicate brain injury and lack of oxygen.
Time to Call 911: If any symptoms are present, call 911. Every minute counts when dealing with a stroke. Note timestamps for stroke symptoms and relay any information to emergency personnel.
The Role of Physical Therapy in Stroke Recovery
Once emergency medical professionals and neurologists can remove the blood clot or stop bleeding in the brain, stabilize patients, and evaluate for any damage or effects from the stroke, they will give patients the clear to start rehabilitation and recovery, usually starting with physical therapy. To regain independence, increase recovery time, and improve a patient’s quality of life, physical therapy helps to address any damages caused by the stroke, giving patients a chance to make a full recovery.
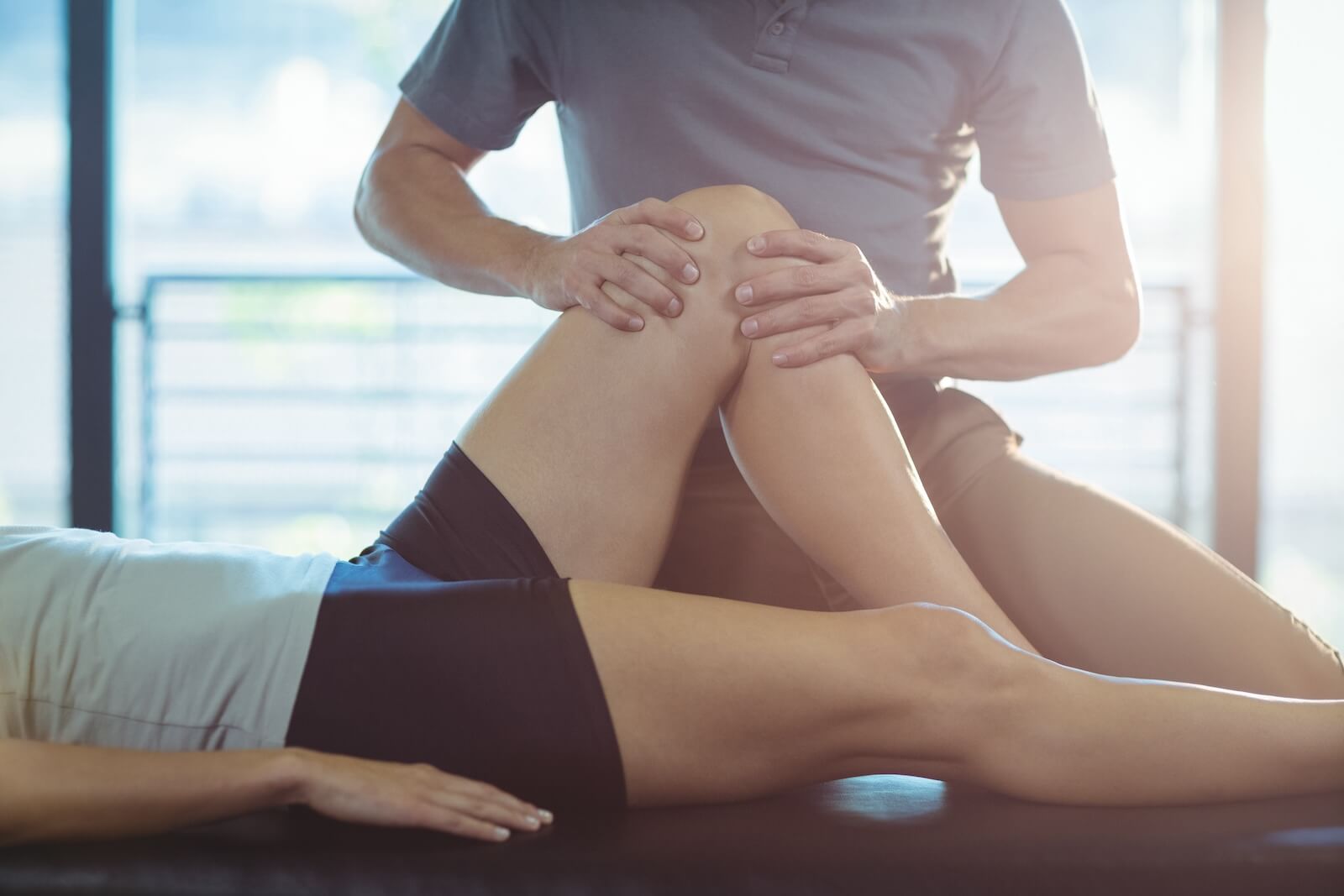
Physical therapy is a specialized form of rehabilitation that helps individuals regain their physical function and improve their quality of life after a stroke. Physical therapists work closely with stroke patients to develop individualized treatment plans that address their needs and recovery goals. By utilizing a series of treatments ranging from strength and coordination training to functional training, physical therapists help patients recover from the damages they may have experienced during a stroke.
Physical Therapy Techniques Used in Rehabilitation
Depending on the individual needs of stroke patients, physical therapists will employ a variety of techniques to restore function and ability in patients during rehabilitation sessions. Some of the methods used by physical therapists include:
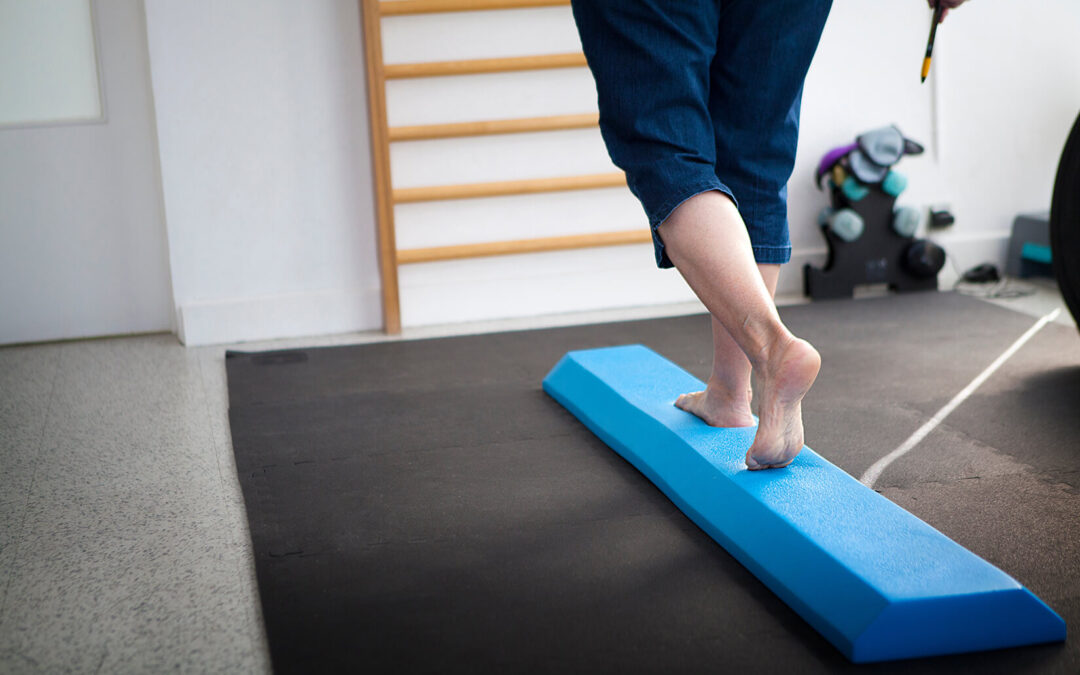
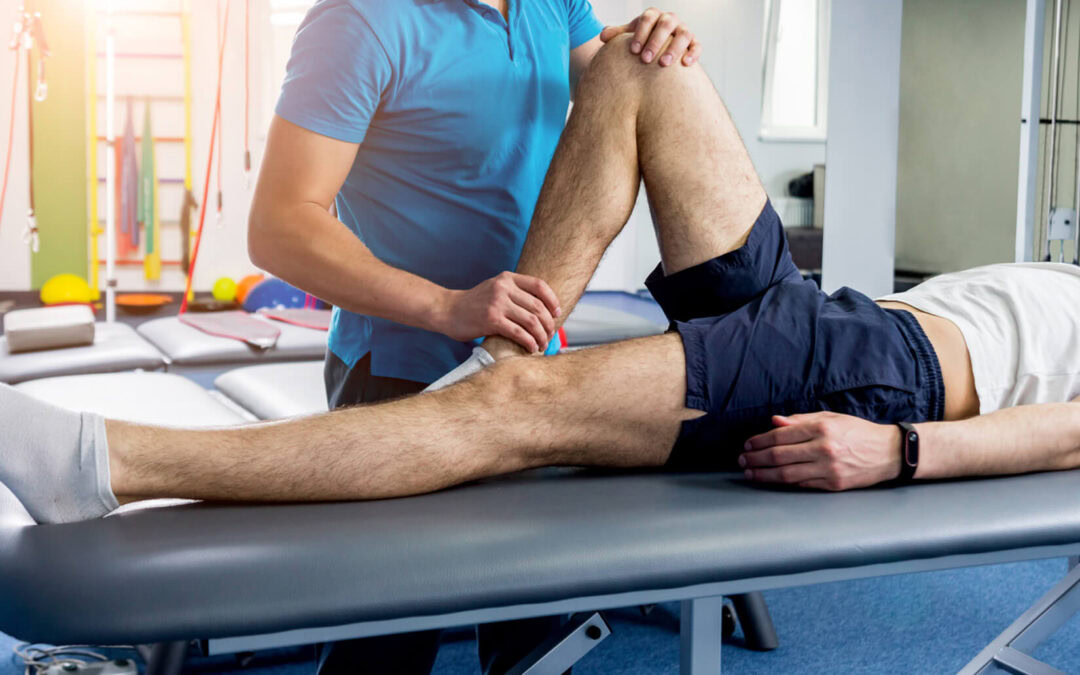
Therapeutic Exercise: Strength training, balance training, gait training, and range of motion exercises are integral components of post-stroke rehabilitation to restore movement and function. Stroke patients often experience difficulties with walking, necessitating therapeutic intervention. Therapists assist with leg strengthening, stability exercises, and assisted walking until patients regain independent mobility.
Manual Therapy: In some instances, massage therapy, joint mobilization, and soft tissue mobilization are employed to alleviate muscular pain and reduce stiffness and rigidity in affected limbs. These techniques aim to relieve muscle pain and enhance blood flow to areas requiring increased healing.
Electrical Stimulation: Electrical stimulation is a therapeutic technique that utilizes electrical impulses to target specific physiological responses. Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES) employs electrical impulses to stimulate muscles, improving strength and function. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS), on the other hand, utilizes electrical impulses to block pain signals and reduce muscle spasms.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention is crucial when addressing a stroke — every second counts from when the stroke occurs to when patients get the green light for physical therapy. Diagnosing and treating a stroke is time-oriented, requiring fast processes and skillful medical knowledge. Receiving emergency medical help at the first signs and symptoms of a stroke allows doctors to restore oxygen to the brain and prevent further damage or even death.
Once doctors deem patients healthy enough to start rehabilitation, starting physical therapy as soon as possible after experiencing a stroke helps the brain to regain function, prevent complications, improve functional outcomes, and enhance the overall quality of life for stroke survivors. Taking the necessary steps to improve patient’s quality of life ensures they live a full and independent life.
Live Independently with Total Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the rehabilitation of stroke survivors. By addressing a wide range of physical and cognitive impairments, physical therapists can help individuals improve their quality of life, regain independence, and reach their full potential after experiencing the effects of a stroke.
Total Physical Therapy utilizes patient-first approaches and customized treatment plans to help patients live fulfilling lives. Using proven and evidence-based techniques, our team of physical therapists provides quick pain relief and heals a wide range of musculoskeletal issues, including stroke effects. Let us set you on the path to total recovery. For more information or to schedule an appointment, visit our website or call (303) 758-5060.